Researchers have released a report detailing how a recent WinRAR path traversal vulnerability tracked as CVE-2025-8088 was exploited in zero-day attacks by the Russian ‘RomCom’ hacking group to drop different malware payloads.
RomCom (aka Storm-0978 and Tropical Scorpius) is a Russian cyberespionage threat group with a history in zero-day exploitation, including in Firefox (CVE-2024-9680, CVE-2024-49039) and Microsoft Office (CVE-2023-36884).
ESET discovered that RomCom was exploiting an undocumented path traversal zero-day vulnerability in WinRAR on July 18, 2025, and notified the team behind the popular archiver tool.
“Analysis of the exploit led to the discovery of the vulnerability, now assigned CVE-2025-8088: a path traversal vulnerability, made possible with the use of alternate data streams. After immediate notification, WinRAR released a patched version on July 30th, 2025,” explains a new report published by ESET today.
WinRAR released a fix for the flaw, which was assigned the identifier CVE-2025-8088, on July 30, 2025, with version 7.13. However, there was no mention of active exploitation in the accompanying advisory.
ESET confirmed the malicious activity to BleepingComputer late last week, which was believed to be used to extract dangerous executables to autorun paths when a user opens a specially crafted archive.
The vulnerability was similar to another path traversal flaw in WinRAR, disclosed a month earlier, tracked as CVE-2025-6218.
ESET’s report explains that the malicious RAR archives include numerous hidden ADS (Alternate Data Stream) payloads that are used to hide a malicious DLL and Windows shortcut, which are extracted into attacker-specified folders when the targets open the archive.
Many of the ADS entries are for invalid paths, which ESET believes were deliberately added to generate harmless-looking WinRAR warnings, while concealing the presence of the malicious DLL, EXE, and LNK file paths deeper in the file list.
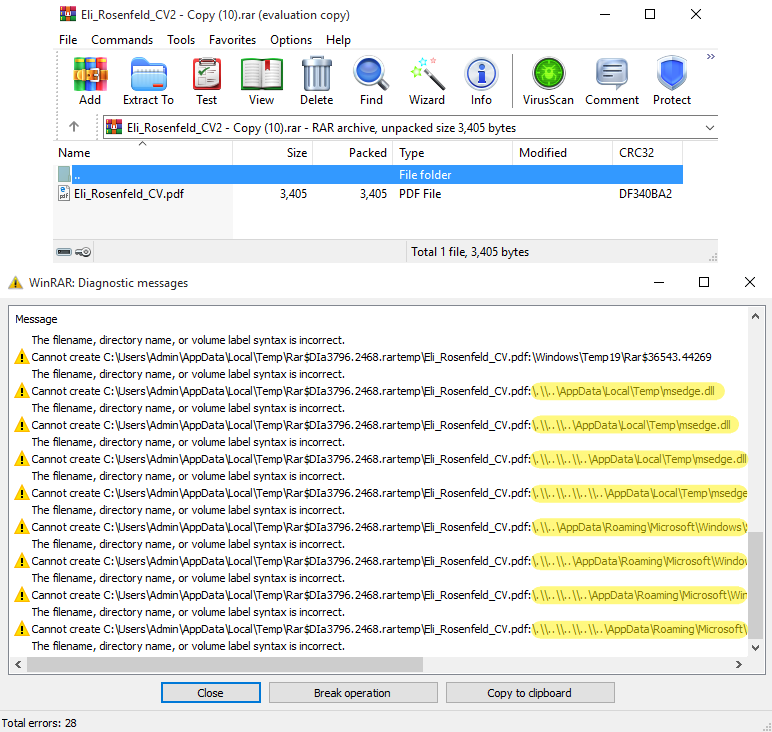
Source: ESET
The executables are placed into the %TEMP% or %LOCALAPPDATA% directories, while the Windows shortcuts (LNK files) are dropped in the Windows Startup directory so that they are executed upon subsequent login.
ESET documented three distinct attack chains, all delivering known RomCom malware families:
- Mythic Agent – Updater.lnk adds msedge.dll to a COM hijack registry location, which decrypts AES shellcode and runs only if the system’s domain matches a hardcoded value. The shellcode launches the Mythic agent, enabling C2 communication, command execution, and payload delivery.
- SnipBot – Display Settings.lnk runs ApbxHelper.exe, a modified PuTTY CAC with an invalid certificate. It checks for ≥69 recently opened documents before decrypting shellcode that downloads additional payloads from attacker servers.
- MeltingClaw – Settings.lnk launches Complaint.exe (RustyClaw), which downloads a MeltingClaw DLL that fetches and executes more malicious modules from the attacker’s infrastructure.
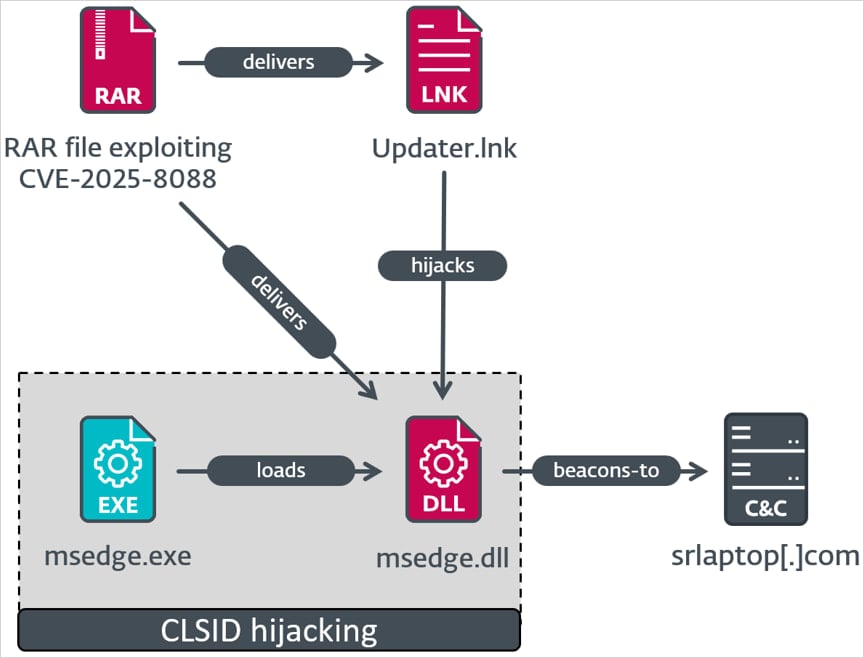
Source: ESET
Russian cybersecurity firm Bi.Zone also reports observing a separate activity cluster, which they track as ‘Paper Werewolf,’ also leveraging CVE-2025-8088, as well as CVE-2025-6218, in attacks.
ESET shared the complete indicators of compromise for the latest RomCom attacks on its GitHub repository.
Although Microsoft added native RAR support to Windows in 2023, the feature is only available to newer releases, and its capabilities are not as extensive as those baked into WinRAR.
Hence, many power users and organizations continue to rely on WinRAR for managing archives, which makes it a prime target for hackers.
RarLab told BleepingComputer that they are not aware of the details of the exploitation of CVE-2025-8088, did not receive any user reports, and ESET only shared with them the technical information required to develop a patch.
WinRAR does not contain an auto-update feature, so users need to manually download and install the latest version from here.


